Every aspect of life is touched by manufacturing, and we rely on the collective intelligence and mindset within the sector to bring us the new and innovative products that sustain us and help us navigate this complicated world. While it can be challenging to think about the future with all of its uncertainties, it is an essential foundation for shaping solid future strategies and investments. The Future of Manufacturing in Illinois is the start of a larger process, that thinks about how to grow and build the vital manufacturing sector in Illinois. It represents a unique opportunity to think about the future in a different way, and to work together to explore, validate and then customize future planning for the sector.
The manufacturing industry is undergoing rapid and exponential change. The revolutionary technologies of Industry 4.0 and its effects on the workplace have transformed the relationship between humans and machines. Will we consume ourselves out of the resources that sustain our consumption economy, or will we be able to make the rapid changes necessary to save the earth’s generous bounty?
FUTURE OF MANUFACTURING REPORT (2016)
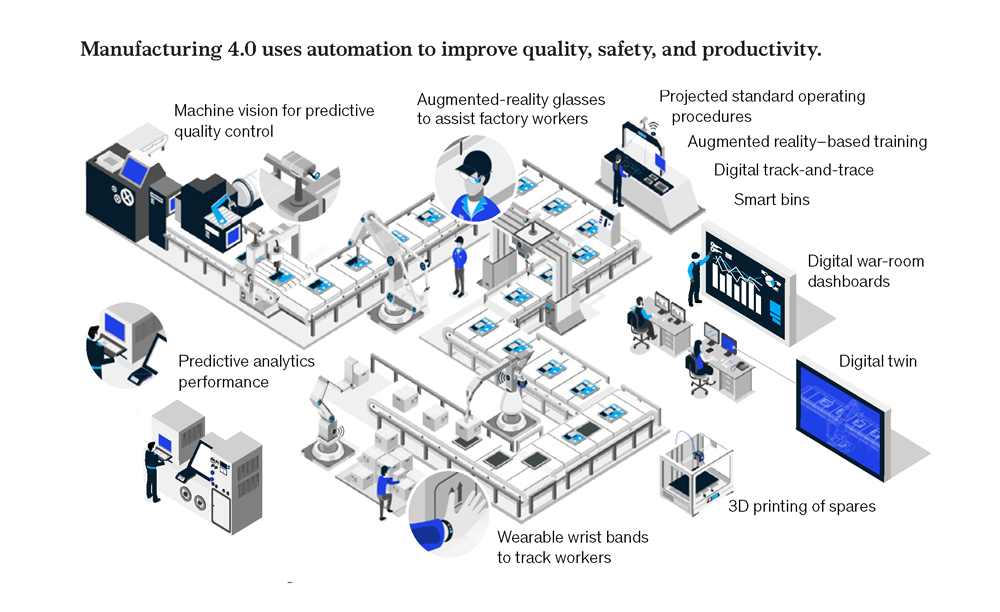
Manufacturing is experiencing the fourth industrial revolution head on as it is driven by a series of shifts in consumer driven markets, technology, workforce and sustainability. Rapid globalisation has developed complex global networks, allowing companies and people to design, source materials, manufacture and distribute products to consumers almost anywhere. The Future of Manufacturing examines current trends and describes the ways in which they are changing companies, processes and communities throughout the world.
MANUFACTURING TRANSFORMED BY TECHNOLOGY
Source: Industrie 4.0: the industrial revolution – guide to Industrie 4.0.
Future iQ predicts that technology will be the critical catalyst of transformational change in manufacturing, and the companies that adapt rapidly to Industry 4.0 technologies will emerge the most agile and sustainable.
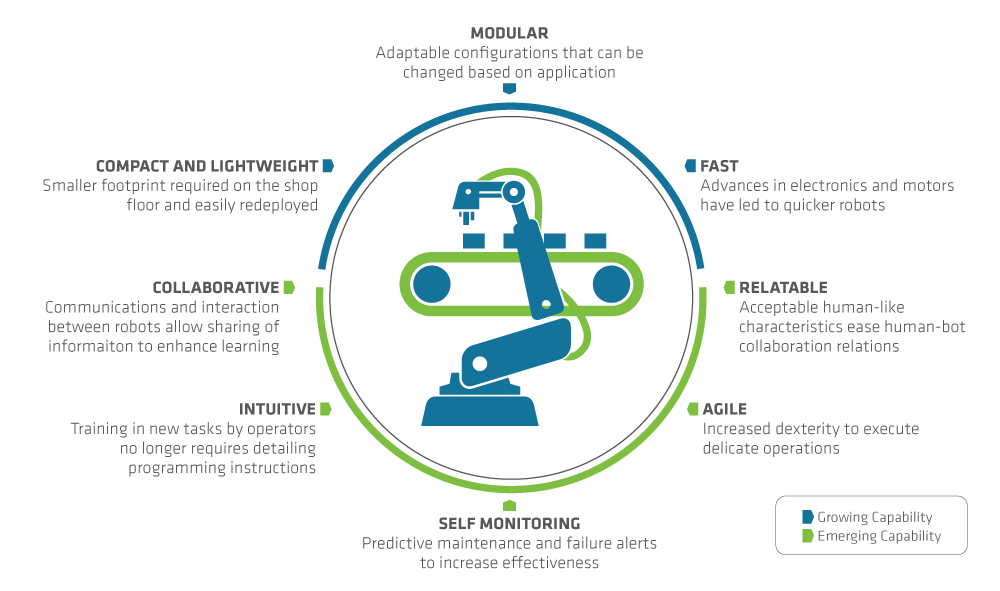
TECHNOLOGY’S REVOLUTIONARY IMPACT ON MANUFACTURING
The necessity for manufacturers to transform their systems through digitisation and new technologies is creating a situation of haves and have-nots worldwide. To manage these impacts, the transition to digitisation will require the collaborative efforts of government, private industry and individual citizens.
Source: International Federation of Robotics. World Robotics: Industrial Robots 2015.
Future iQ Predictions
- Intelligent factories will reach beyond factory walls, with supply chains, production plants, products and logistics all interconnected within the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
- The impact of nanotechnology on society has been compared to the invention of electricity or plastic – it will transform nearly everything we use today.
- With the advent of highly flexible, individualised and resource efficient mass production, customised products will be produced in the same timeframe as standard products at a marginal increase in cost.
- The future of additive manufacturing will see this technology proliferate in scale and scope, moving from prototyping and design to full scale production.
Smart technologies will allow manufacturers to use predictive analytics to rapidly enhance the speed and accuracy of production systems.
RESOURCES – THE ELEMENTS THAT SUSTAIN US
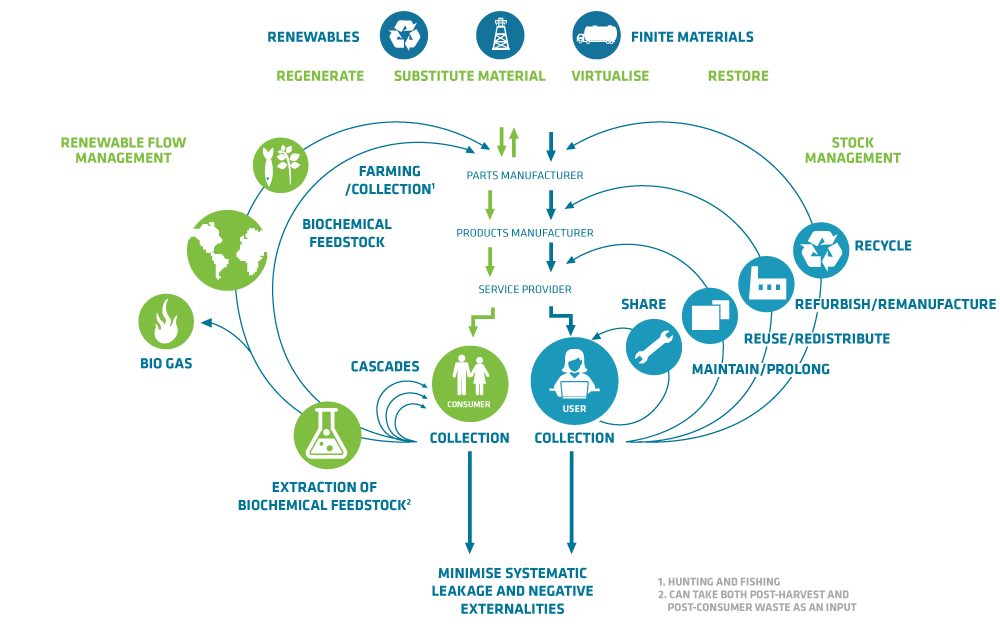
With the growth of the global middle class, consumer demand is skyrocketing and there is increasing pressure on the raw materials required for manufacturing. As the availability of many new or ‘virgin’ sources of materials either become scarce or economically infeasible to extract, manufacturing is seeing sustainable materials management of post-consumer sources as a way of reclaiming raw materials in a circular economy model.
Source: Ellen MacArthur Foundation, SUN and McKinsey Center for Business and Environment; Drawing from Braungart & McDonough, Cradle to Cradle (C2C).
Future iQ Predictions
- Shifting from a linear path of production to a circular process will improve resource productivity and allow goods to be manufactured while maximising the efficient use and reuse of materials and energy, and minimising the cost, as well as the environmental and social impacts of resource extraction and processing.
- With global demand for water projected to increase by 55% by 2050, where it is possible to reclaim, treat and reuse water repeatedly, there will be the best possibilities to maintain consistent quality supplies for all water users.
- Energy efficiency, resource recovery and reuse, and intelligent design principles will influence most capital investment decisions as countries place priority and offer significant incentives for sustainably focused enterprises.
- Increasing worldwide energy demands will prompt countries and companies to seek affordable, clean, renewable energy strategies and effective energy policies.
The COVID-19 pandemic has put a spotlight on the strengths and weaknesses of manufacturing’s heavy reliance on global supply chains and humans in the workplace.
THE EVOLVING WORKFORCE – HUMANS AND MACHINES
An aging demographic is critically affecting the supply of skilled workforce in the manufacturing industry. This trend, combined with the impacts of COVID-19, is placing manufacturing on a fast track to adopt Industry 4.0 technologies that replace humans and accelerate automation in the workplace.
Source: Mayank Agrawal, Karel Eloot, Mattea Mancini, and Alpesh Patel. Industry 4.0: Reimagining manufacturing operations after COVID-19, McKinsey & Company, July 2020.
Future iQ Predictions
- The future of manufacturing will become increasingly automated, complemented by a small but highly skilled workforce and will be less dependent on the use of large numbers of physical laborers.
- Increasing demographic pressures including the effects of COVID-19 will lead to a larger focus on skills and productivity in combination with increased technological support such as automation. The image of human teams working alongside robotic production lines will become commonplace.
- Jobs will be eliminated due to automation however other more highly skilled and higher paying will be created. Very few occupations will be automated in their entirety in the near or medium term, but some activities will be automated, redefining the jobs of many workers.
- Leveraging the potential of women in the manufacturing workforce will be a foundational piece of accessing adequate workforce levels for the industry.
Driven by necessity, a reinvigorated culture of innovation is permeating the manufacturing industry. Innovation zones, districts, hubs and corridors are occurring across the globe as the value of connectivity and proximity enable solutions to critical needs to be discovered in collaborative environments.
MANUFACTURING OF THE FUTURE – HOW, WHAT, WHEN, AND WHERE?
Manufacturing networks of innovation excellence are likely to expand and include collaborations in logistics, value chain distribution, and support services. Successful firms will embrace the benefits that these types of partnerships can bring.
The manufacturing industry will become an interconnected network with limitless potential to provide innovative products and services to all regions of the world.
Future iQ Predictions
- The location and configuration of production facilities will be driven less by access to inexpensive physical labor or raw materials and driven more by access to a skilled workforce, logistics infrastructure, and end markets.
- The movement towards open sourcing will see the pace of innovation and diffusion accelerate within the manufacturing sector.
- Supply chains will evolve into value chains where firms involved in both production and service activities will be connected as vital linkages in the primary process flow and feedback comes from all parts of the chain from suppliers through to customers.
- Increasing global populations in less developed nations will intensify the need for manufactured goods and will change where economic centres and markets are located thereby presenting opportunities for manufacturers to access large new markets.