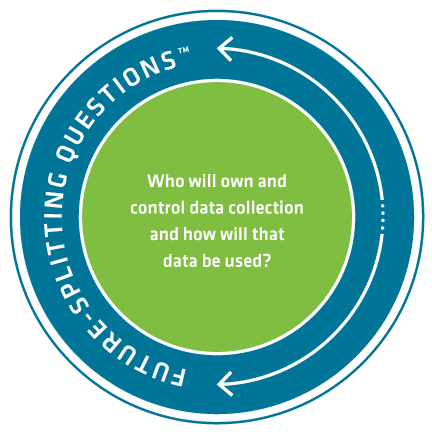
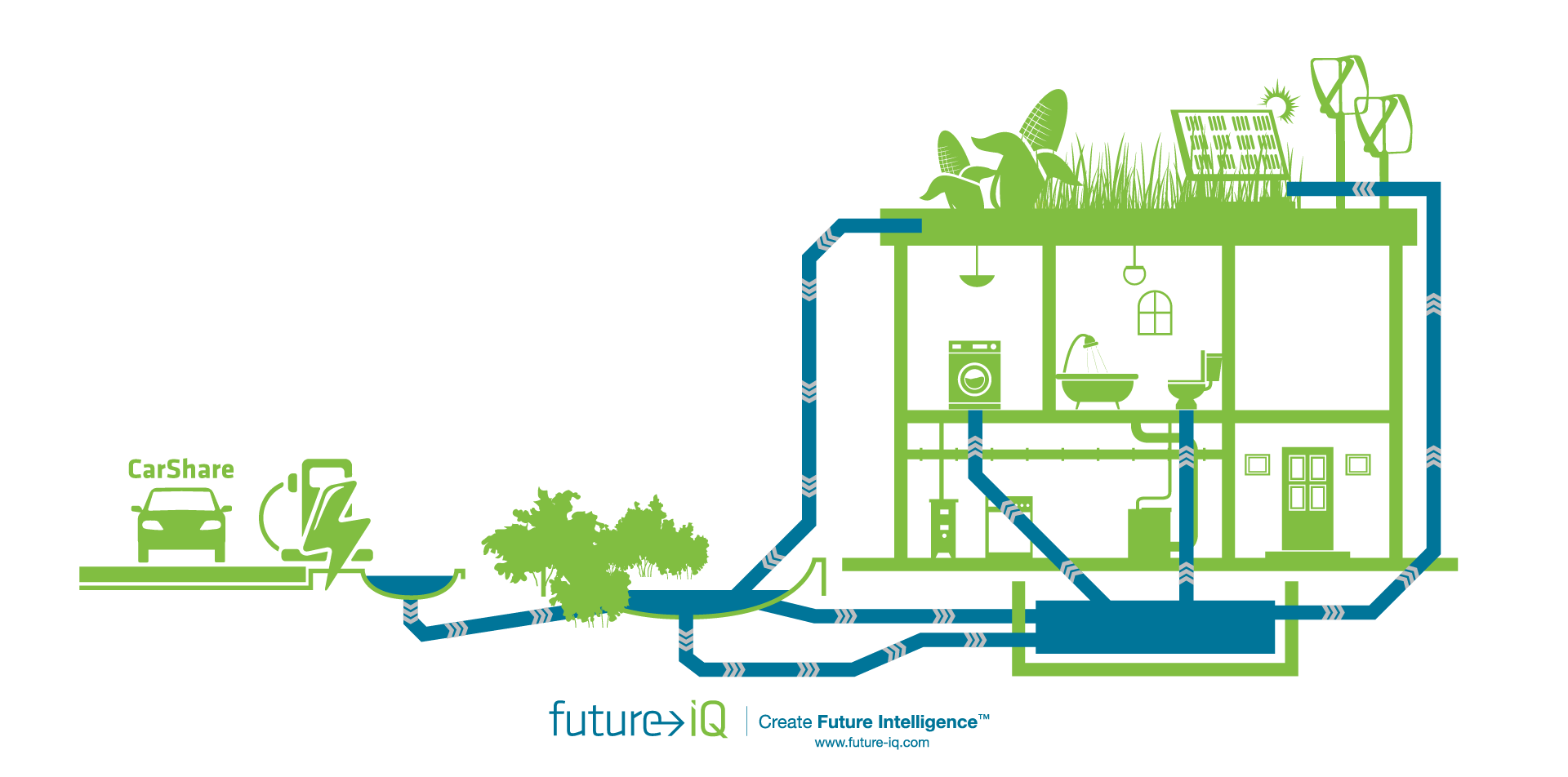
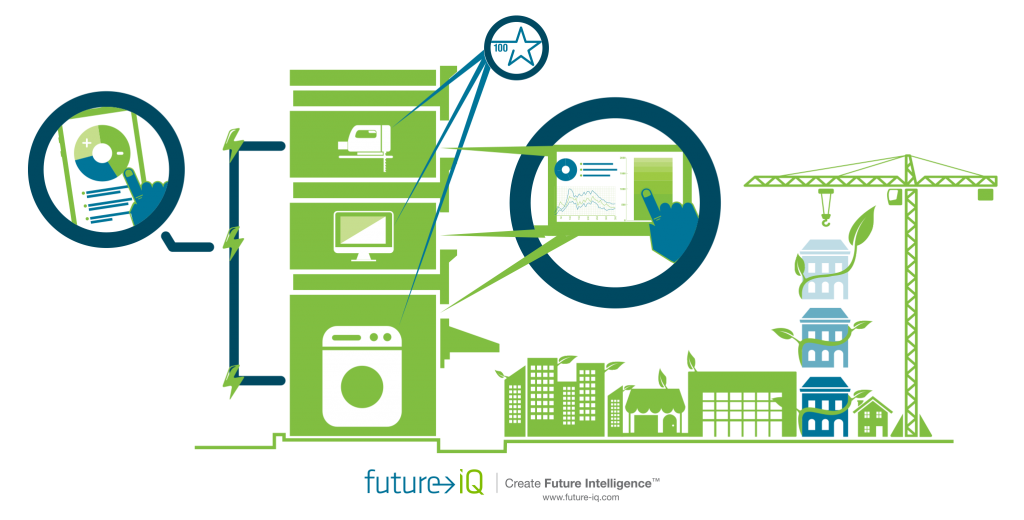
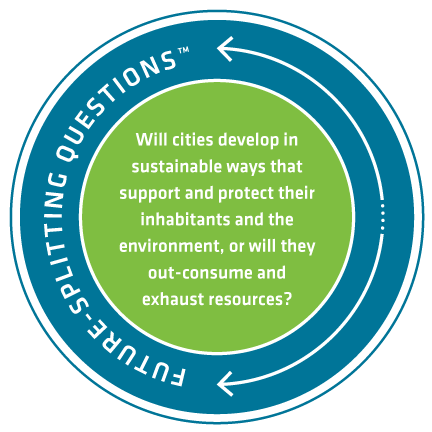
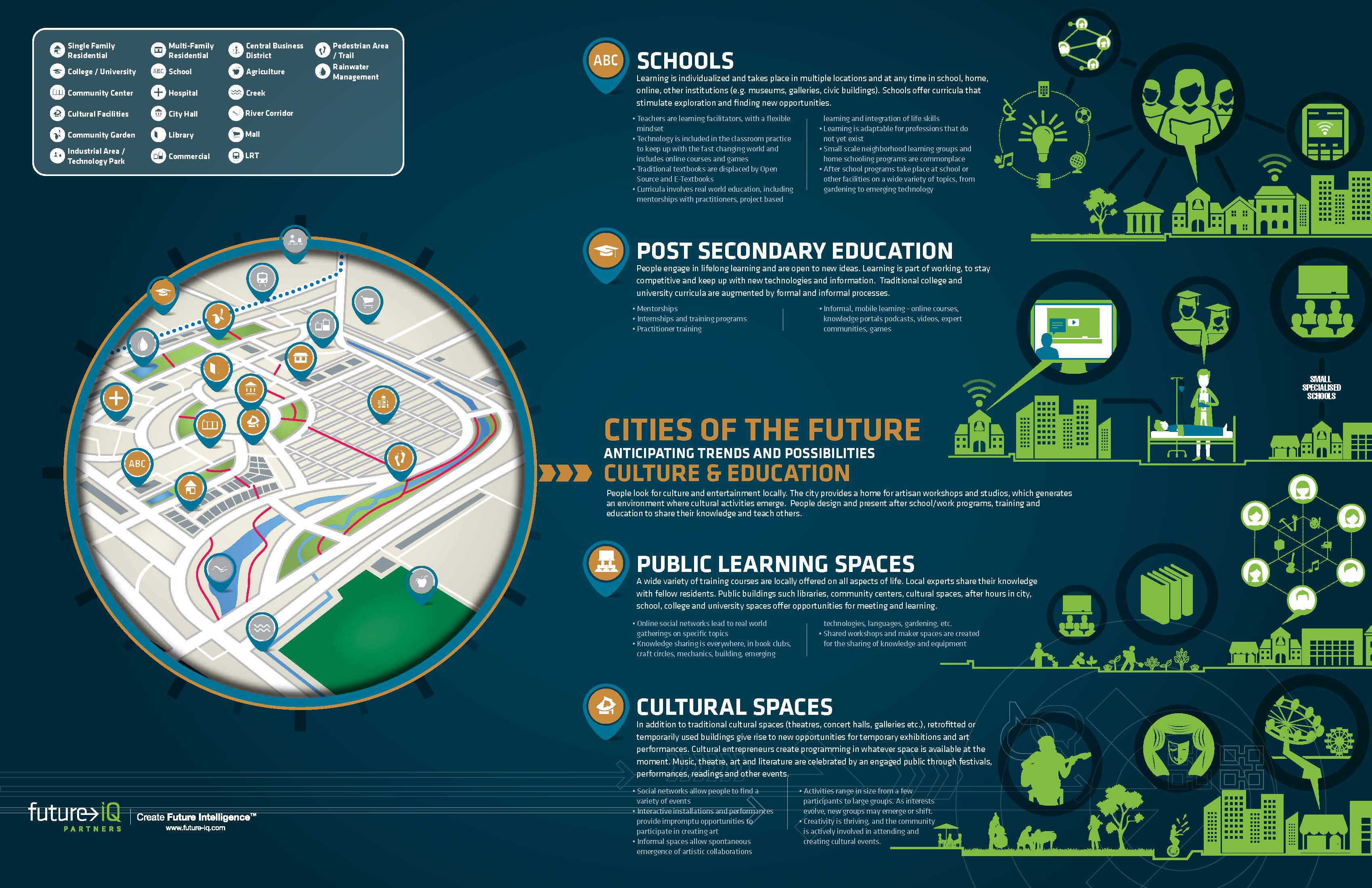
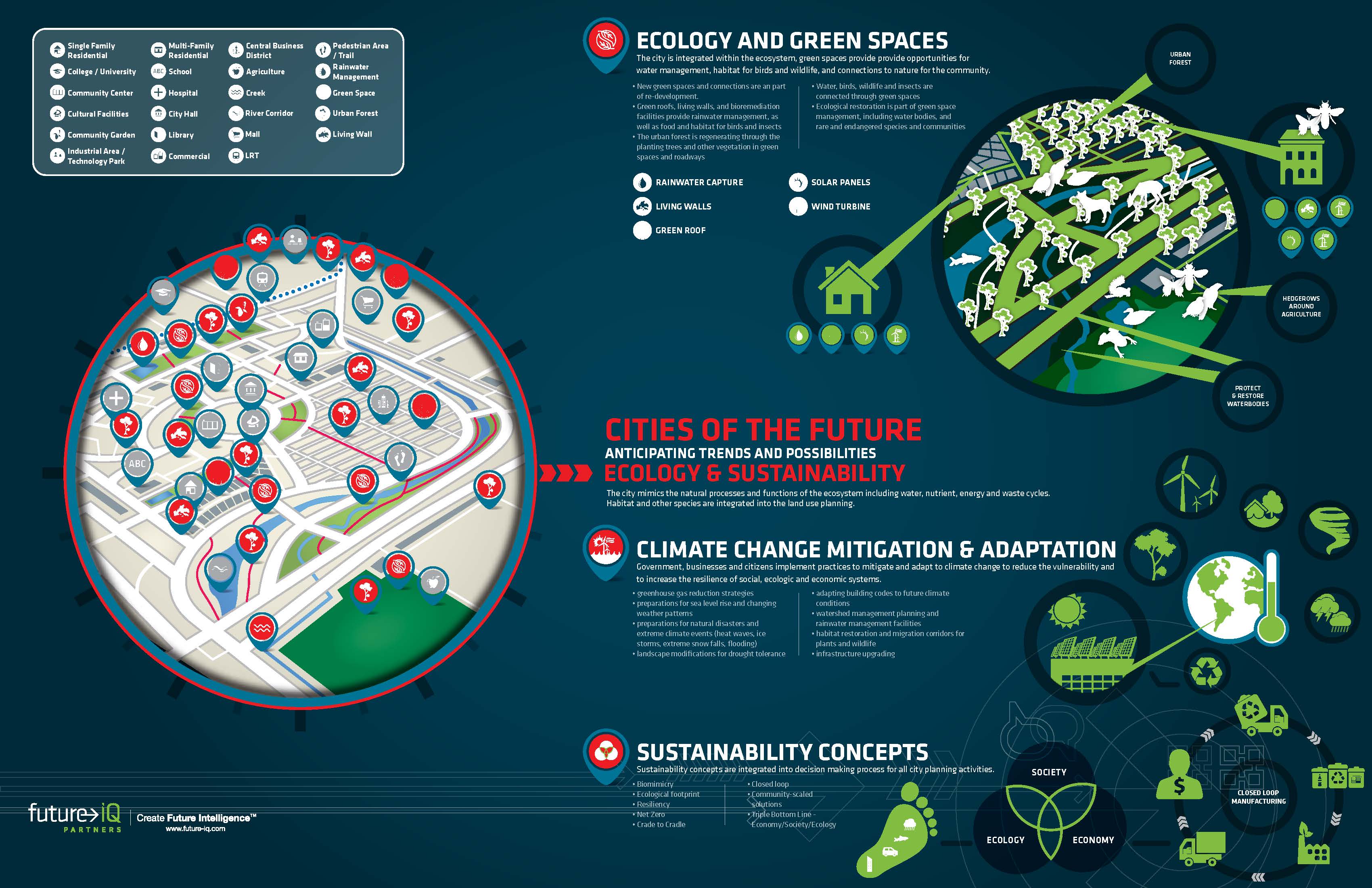
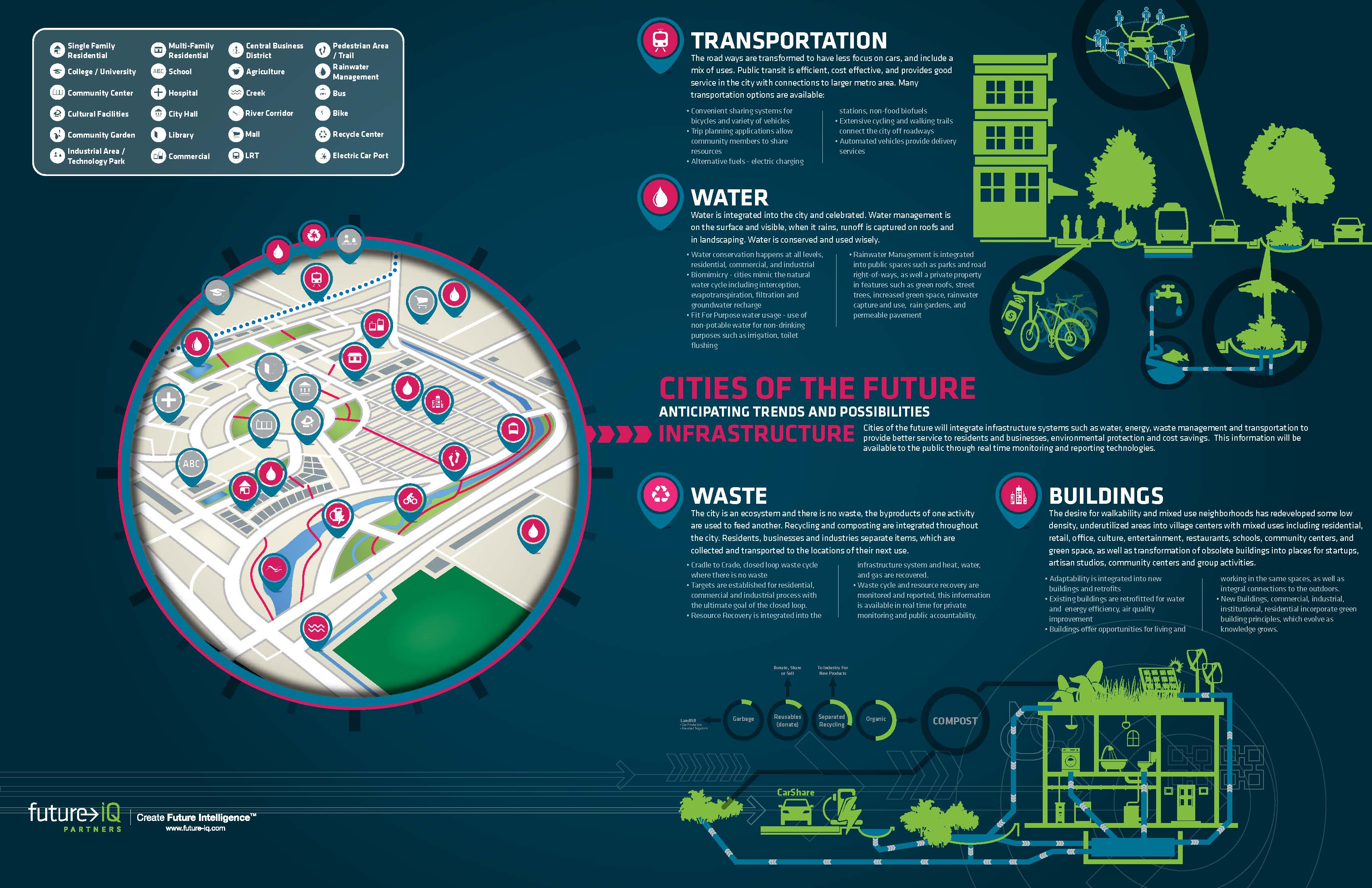
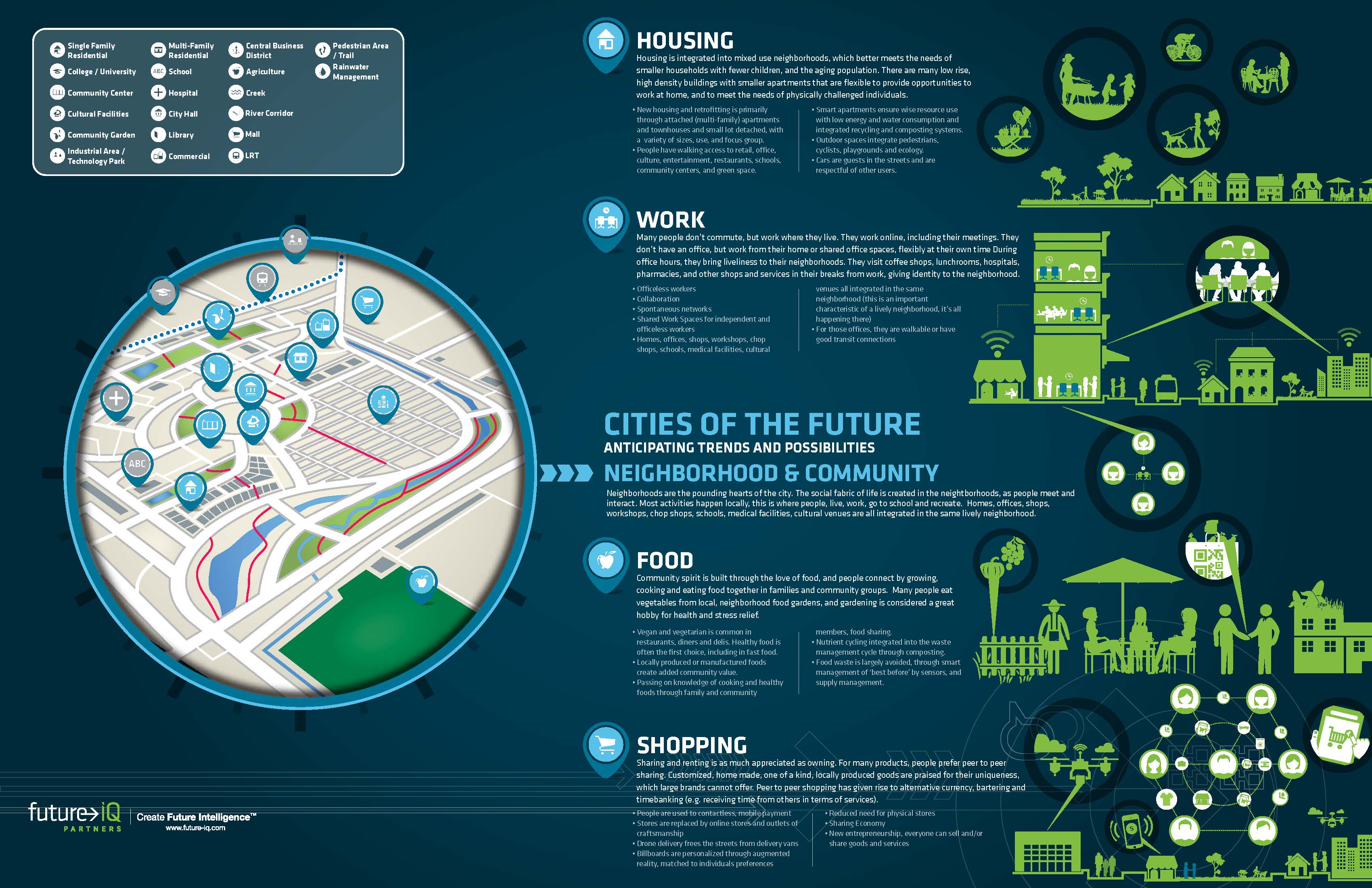
The exponential growth of cities and regional areas will have a critical impact on ecosystems worldwide. Cities of the Future – Anticipating Trends and Possibilities was produced by Future iQ in 2015 and provides an in-depth look at emerging trends impacting cities and the communities within them. This publication is meant to be a resource for people to use to anticipate what may be possible in their own cities as they explore and meet the challenges and opportunities that lay ahead.
Future iQ predicts that cities will lead the way in meeting the current challenges of poverty and public health with innovative holistic change that addresses the inequities and inequalities of the past to meet the additional challenges of a post-COVID world.